c-Myc mRNA biology modulators
Progress level
69%
Text with media
Rich text
c-Myc is an oncoprotein, which is considered one of the most attractive cancer targets, as it is upregulated in most types of tumors (epithelial, hematopoietic, central nervous system). The inhibition of c-Myc has been shown to reduce tumor growth and/or survival. However, after decades of failures to directly target this protein, c-Myc remains an “undruggable” target.
Status title
Status
Status bullet list
- A novel approach to target the undruggable c-Myc oncogene in Cancer – reducing c-Myc protein translation. Compounds were identified which markedly reduced c-Myc protein levels in lung tumor cells.
- We monitor c-Myc translation by using a pair of labeled tRNA isoforms. This pair is unique to c-Myc mRNA over the mRNA repertoire in target cells and is therefore its “signature” pair.
- A diverse library of 100,000 compounds was screened, generating a set of 20 million images. The resulting big data was analysed in our cloud-based platform using proprietary image analysis and machine learning algorithms identifying “hits”, which are compounds that are actively inhibiting the production of c-Myc, but do not affect general protein synthesis.
- Compounds from three selected clusters exhibiting c-Myc-dependent activity and highly cytotoxic in c-Myc-addicted tumors, compared to cells with normal c-Myc expression level. These and other compounds make c-Myc hits favorable drugs.
Image title
1. PSM Screen: Target-specific tRNA pair
Image description
2.3 million images generated per screen
Automatic generation of a clean FRET image
Automatic generation of a clean FRET image
Image

Image title
2. High content, cloud-based image analysis
Image description
Data generated for 54 million cells
90 different features
Total of 5 billion data points
90 different features
Total of 5 billion data points
Image
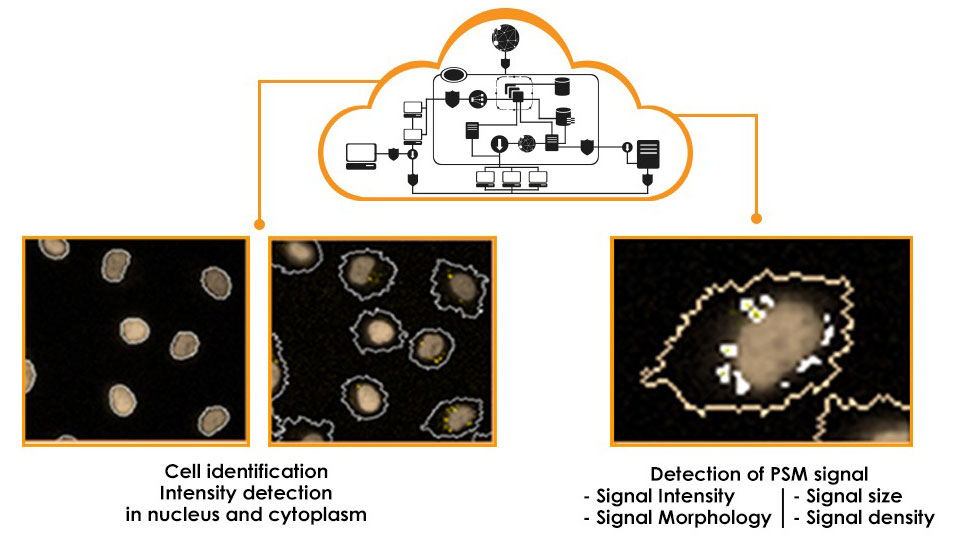
Image title
3. Hit Identification: Big data analysis
Image

Image title
4. C-Myc translation inhibitors
Image description
Hits reduced c-Myc protein levels in a dose dependent manner
Image

Rich text
Hit compounds reduce c-Myc protein. Compound activity that reduces c-Myc protein expression was examined using immunofluorescence staining.
Progress title
Oncology
Progress subtitle
c-Myc tumors
Order
-16
Display program page